My late mother, then Elizabeth Willett, was almost 14 in June 1944. In her memoirs she wrote of her memories of D-Day. She was away at boarding school in Sherborne, Dorset.
During the night of the 5th – 6th of June 1944, everyone in my house was woken by the staff and prefects to watch the gliders being towed over to Normandy at the start of D-Day.
I’ve always been grateful that we were made to watch this historic moment. The silhouettes of the gliders and their tow-planes were etched blackly against a crystal clear night sky; even the individual tow-lines were visible. For what seemed an incredibly long time this massive air armada roared overhead and, when they had finally disappeared, the sound of the towing planes still seemed to pulse in our ears as we tried to settle back to sleep.
Next morning we could hear the naval bombardment quite clearly, and were horrified when we realised how close the Germans had come.
There were three service hospitals nearby, and we watched the military ambulances across the valley winding their way down the hill every evening. Soon a long hospital train would snake into view and stop at the local station. Later on, the ambulances began the slow crawl back up the hill, taking the wounded to the hospitals. It was a moving sight and another we will never forget.
Faulder, EP., Unpublished Memoirs (with minor amendments)
Presumably an alert teacher noticed the first gliders going over and realising what was happening decided to rouse the pupils so they would have that memory.
The D Day Airborne Operations
In pondering which mission my mother saw a number of factors have to be taken into account.
- Who they were
- Where they where flying from
- When they flew
- What size of forces flew
Both British and American parachutists and gliders took part in the various airborne operations.
Operation Tonga was the British operation and flew from RAF Tarrant Rushton in a number of phases.
At 22:56 on the night of 5 June, … six Handley Page Halifax heavy bombers took off from RAF Tarrant Rushton towing six Horsa gliders carrying the coup-de-main force. … Flying over the English Channel at 7,000 feet (2,100 m), the bombers crossed the Normandy coast at 00:07 on 6 June, 1944 and released their towed gliders. …. [They] captured what are now known as the Pegasus and Horsa Bridges.
(Operation Deadstick – ref a well sourced article on Wikipedia.)
A few minutes later the parachute pathfinders took off, followed by the main parachute force.
[Just before midnight] the remainder of the transports carrying the division began to take off. This wave was divided into three groups. The first consisted of 239 Douglas Dakota and Short Stirling transports as well as seventeen Horsa gliders, carrying the bulk of the 3rd and 5th Parachute Brigades and their heavy equipment. These forces were due to land in their respective drop-zones at 00:50. The second group was destined to land at 03:20, and consisted of sixty-five Horsa and four Hamilcar gliders transporting the divisional headquarters and an anti-tank battery. The final group was formed of three Horsa gliders carrying sappers and men from the 9th Parachute Battalion, who were to land atop Merville Battery at 04:30.
(Operation Tonga – ref a well sourced article on Wikipedia.)
RAF Tarrant Rushton is about 20 miles East South East of Sherborne. At first sight this might seem to rule out these flights as being the ones seen over Sherborne. However that night the wind was coming in from the North West, so bombers towing gliders would have wanted to take off in as near a North Westerly Direction as possible.
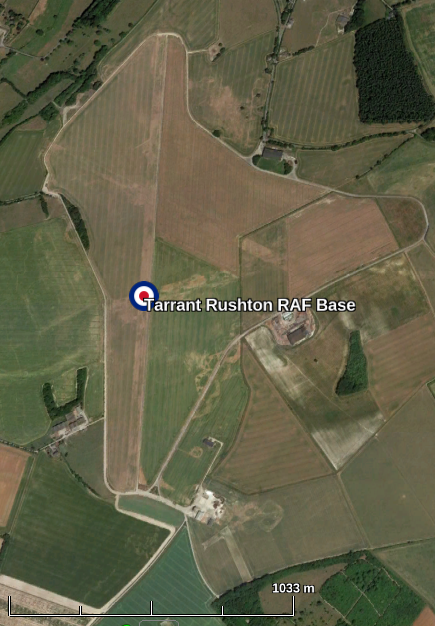

© Google Earth
From the above, modern aerial photograph, the shadows of three runways can be seen in the classic overlapping triangle formation. The most visible runway is the one running North South, but other runways can be seen running approximately North West – South East and North East – South West. It is likely that on the night they would have taken off either North West bound or possibly North bound as that runway appears longer.
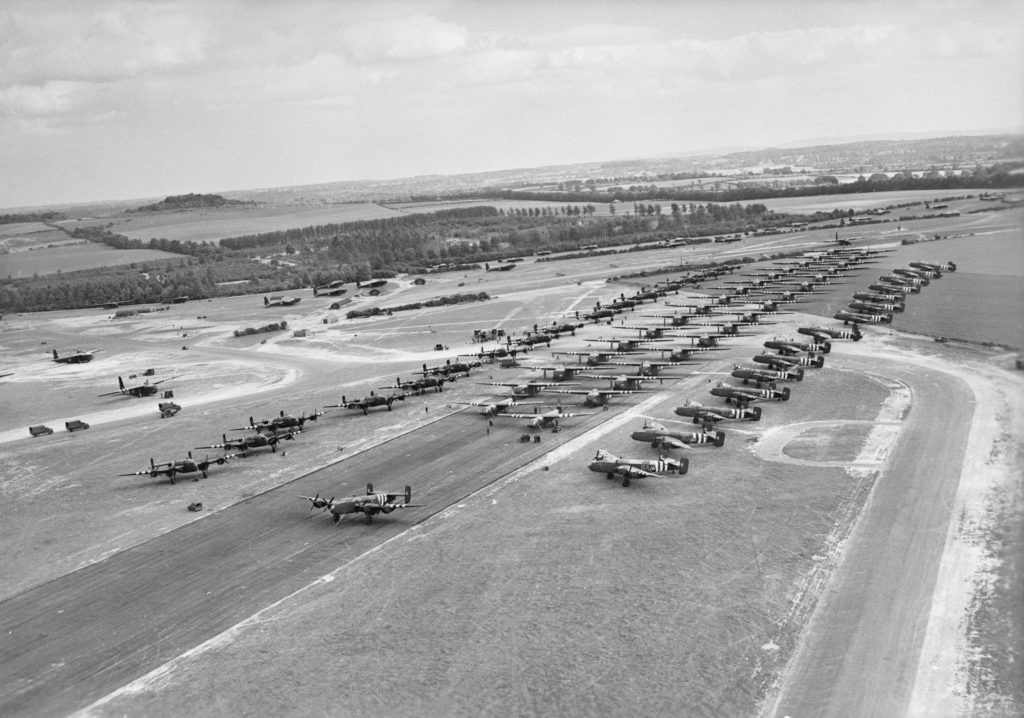

This is photograph CL 26 from the collections of the Imperial War Museums., Public Domain
I believe (from the layout of taxiways) that the picture above shows the southern end of the North-South runway. The caption does not indicate whether these are aircraft waiting the day before, or whether they are the reinforcement Operation Mallard which took off in the afternoon of D-Day and involved 256 gliders leaving Tarrant Rushton in three phases.
It is possible that in forming up, these forces flew over Sherborne; however the Overview map of the Invasion (below) tends to indicate that the British 6th Airborne Division approached the Eastern Beaches (The British and Canadian ones – Gold Juno and Sword) from the North (flying out over the Sussex coast) – which would imply flying east after taking off.
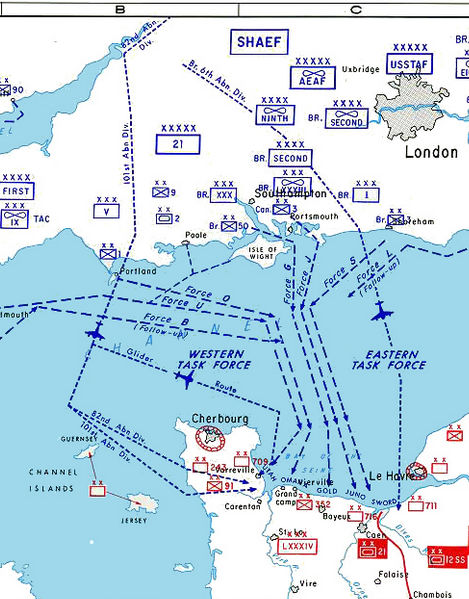
Rights: Wikimedia Commons
The American glider operations took off from further East:
- From RAF Aldermaston – Mission Chicago – 101st Airborne Division in 52 CG-4 Waco gliders leaving from 01:19 onwards, due to land at 04:00 on D-Day, 2 hours before dawn.
- From RAF Ramsbury – Mission Detroit – 82nd Airborne Division in 52 CG-4 Waco gliders, also due to land before dawn on D-Day.
The previous map shows they they would have got into formation over Southern England before heading out over the Isle of Portland. This might have taken them over or near Sherborne.
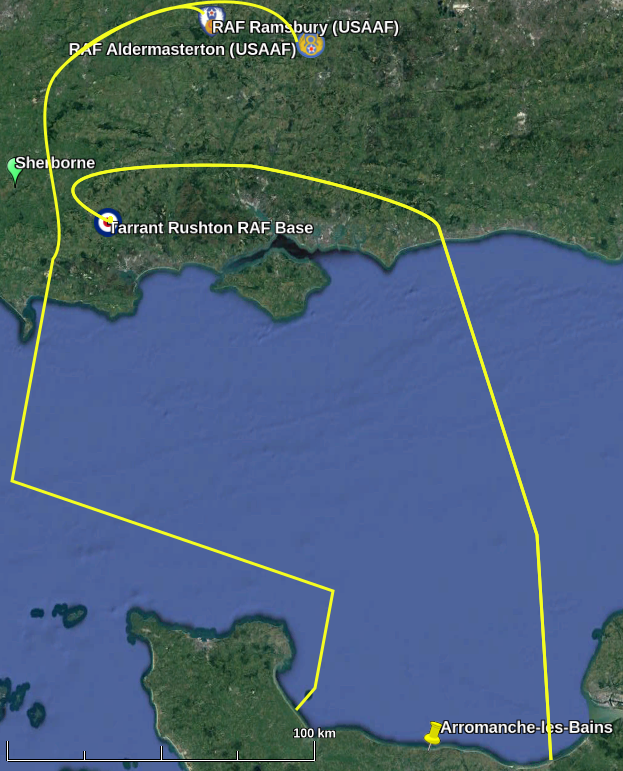
in order to be consistent with the previous Invasion map
Underlying Map © Google Earth
The British overnight force consisted of:
| Take off Time | Aircraft | Purpose | Landing Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22:56 D-Day – 1 | 6 Handley Page Halifax Bombers towing 6 Horsa Gliders | Deadstick Parachutist Force to capture the bridges over the Caen Canal and Orne River | 00:16 to 00:21 D-Day |
| Between 23:00 and 23:20 D-Day – 1 | 6 Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle transports 16 Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle transports | Tonga Pathfinder Pathfinder Parachutists Main Parachute force to attack Caen | |
| 23:50 D-Day -1 onwards | 239 Douglas Dakota and Short Stirling transports 17 Horsa Gliders | Tonga Phase 1: Parachutists and Glider Troops | 00:50 D-Day |
| 65 Horsa, 4 Hamilcar Gliders 69 Towplanes | Tonga Phase 2: Divisional Headquarters and anti-tank battery | 03:20 D-Day | |
| 3 Horsa Gliders 3 Tow Planes | Tonga Phase 3: Glider Troops to attack Merville Battery | 04:30 D-Day |
Source Wikipedia – as previously quoted
The American overnight force consisted of:
| Take Off Time | Aircraft | Purpose | Landing Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01:19 D-Day RAF Aldermaston | 52 CG-4 Waco gliders 52 C47 Tow Planes | artillery reinforcement mission | 04:00 D-Day |
| 01:19 D-Day RAF Ramsbury | 52 CG-4 Waco gliders 52 C47 Tow Planes | reinforcement mission | 04:07 D-Day |
Source Wikipedia – as previously quoted
In addition about 13,000 American Parachute Troops landed in the Cotentin Peninsula of France between 0O:20 and 02:44 as Missions Albany and Boston flying from Airfields spread across the South of England (but not the Glider stations previously mentioned).
My mother remembers a glider force with a significant number of gliders. She also recalls the tow lines. Apart from meaning they must have been fairly close to Sherborne (“this massive air armada roared overhead”), it is unlikely that it would have been a mixed force – in which case she could have noticed that it was a mixed force.
This would indicate that it was unlikely that she saw the first Deadstick force of six gliders. If she saw a British Force it would have been the second phase of the main force (69 gliders) which probably took-off around 02:00 to 02:20. (Their take-off times have not been found, but a transit time of about an hour to an hour 20 minutes for other phases, permits an estimate to be made.) However the British craft might have been flying in a direction other than South – which might have been remarkable to a young girl told they were gliders flying to invade France.
However it is more likely that she saw the American Forces from Aldermaston and Ramsbury – which probably appeared as a single continuous flight of 104 Gliders and their tow-planes. This was not a mixed force, it was a significant number of gliders and if it crossed the coast around Portland it might have flown close to Sherborne.
It is possible that earlier possibly more distant operations had alerted teachers that something was happening, so that when a major force flew over they could quickly decide to rouse their charges.
Regrettably, I have had to switch off the commenting on this particular post. It seems that robotic spam generators are triggered by certain phrases in this post – more than half the total level of spam comments received are “comments” on this post. If you are human you should be able to find on this site a means to communicate with me. Just put “Comment on: ” followed by the title of this post in the subject line of an email. Thanks and sorry.
